What is Uveitis?
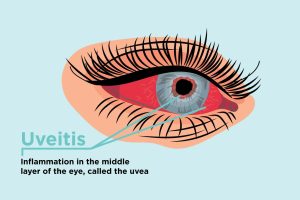
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye that consists of the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. This condition can lead to swelling, tissue damage, and ultimately, vision loss if not treated promptly.
Causes
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
Infections: Such as herpes, syphilis, and tuberculosis.

Eye Injuries: Trauma to the eye can trigger uveitis.

Unknown Causes: In many cases, the exact cause remains unidentified.
Symptoms


Eye Redness: One of the most noticeable symptoms.
Eye Pain: Can range from mild discomfort to severe pain.
Blurred Vision: Difficulty seeing clearly.
Light Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light (photophobia).
Floaters: Dark spots that drift across the field of vision.
Diagnosis
Comprehensive Eye Exam: Includes checking the inside of the eye for signs of inflammation.

Blood Tests: To identify underlying causes like infections or autoimmune disorders.

Imaging Tests: Such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) or fluorescein angiography to get detailed images of the eye.
Treatment

Steroid Eye Drops: To reduce inflammation.

Oral Medications: Steroids or other anti-inflammatory drugs.
Immunosuppressive Agents: For severe cases or when steroids are ineffective.
Treating Underlying Causes: Addressing infections or autoimmune disorders contributing to uveitis.
Preventive Measures

Regular Eye Exams: Essential for early detection and management of RVO and related conditions.
Protect Eyes from Injuries: Use protective eyewear in risky situations.

Manage Health Conditions: Keep autoimmune disorders and infections under control.
Conclusion
Uveitis is a serious eye condition that requires prompt medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent vision loss. Regular eye exams and managing underlying health conditions can help in the prevention and management of uveitis.

